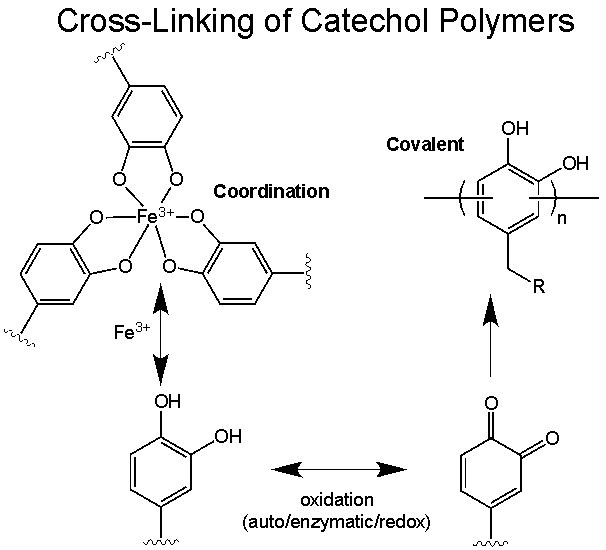
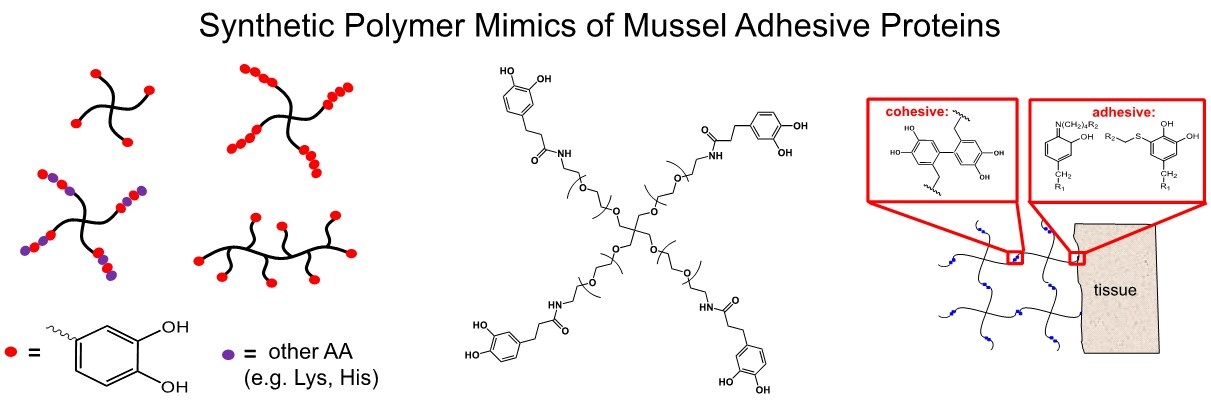
We exploit information gained from our basic studies of mussel adhesion for the design of synthetic adhesives. Typically, synthetic polymers are chemically derivatized with catechols in the form of DOPA, DOPA peptides, or DOPA-mimetic functional groups (Figure). This approach allows us to employ standard polymer synthetic strategies and to confer the important properties of catechols into these polymers in a straightforward and cost-effective manner. The roles of the catechol in these polymers are the same as in the native mussel proteins, namely interfacial adhesion and cross-linking.